Today we are here to learn about some methods to read a text file using Python. Before getting started, make sure You have installed your python IDLE shell and the pip package installer. Else You can work on your command prompt by following our code snippets.
Before getting started, Let’s have quick look at what a text file is.
A text file contains only text and has no special formatting such as bold text, italic text, images, etc. The text files are identified with the .txt file extension, as shown in the example below.
We can manually read, write and manage data in a text file by opening it on our desktop. But Today, We are going to learn how to read the same text file using python. To do So, We need to use a special python module known as the pandas module. Before getting deeper into it, Let’s understand what a pandas module is.
pandas Module
Pandas is an open-source Python library or module that provides in-built high-performance data structures and data analysis tools. It is most preferably used to analyze data along with two other core python libraries- Matplotlib for data visualization and NumPy for mathematical operations.
We are going to install this module in the same way as our previous module using the pip installer as follows.
C:\Users\pc> pip install pandas
The above code snippet will install the pandas module for us as follows.
Using this pandas module, We are going to apply the two most commonly used methods to read our text files as follows.
pandas.read_csv ()pandas.read_fwf ()
Let’s understand those methods with their appropriate syntax followed by some examples in our code snippet.
pandas.read_csv ()
The read_csv() method reads values in a text file, where the delimiter is a comma character. A Delimiter is a character that identifies the beginning or the end of a character string (i.e. nearly like a separator). The Syntax for this method is:
dataframe_name = pandas.read_csv(‘filename.txt’, sep=’ ‘, header=None, names=[“Column1”, “Column2”])
The parameters in the above code snippet are:
- filename.txt: The location of the text file that is going to be read.
- sep: It may be a comma, single space, double space, etc. It’s the Separator between two components in a text file. It’s optional.
- header: This is also an optional field. By default, it will take the first line of the text file as a header. If our file contains no header then we can apply “
header=None” and then it will create the header on its own. - names: We can assign column names while importing the text file by using the
namesargument When there is no header. We can only use it when we do not have headers in our text file. So it’s also an optional parameter.
Example 1
Suppose We have a text file as follows.
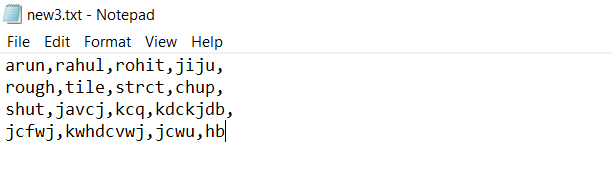
We will read this file with pandas.read_csv () method as follows.
# Importing pandas module as pd
import pandas as pd
# Read our text file into DataFrame df
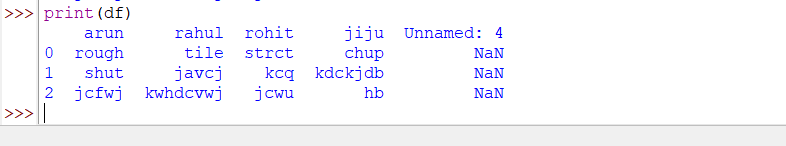
df = pd.read_csv("C:\\Users\\pc\\Desktop\\folder\\new3.txt")
# Show dataframe
print(df)
The above code snippet will give the output as follows.
Example 2
Let us take another text file as follows.
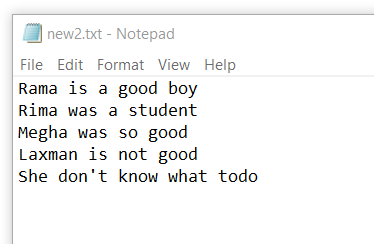
As We can see, there is no header in our text file. We will read this file with pandas.read_csv () method by passing the parameter “header=None” and specifying column names as A, B, and C as follows.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv("C:\Users\pc\Desktop\folder\new2.txt", header=None, names=["A", "B", "C"], sep=" ")
print(df)
The above code snippet will give the output as follows.

Example 3
Let us take another text file as follows.
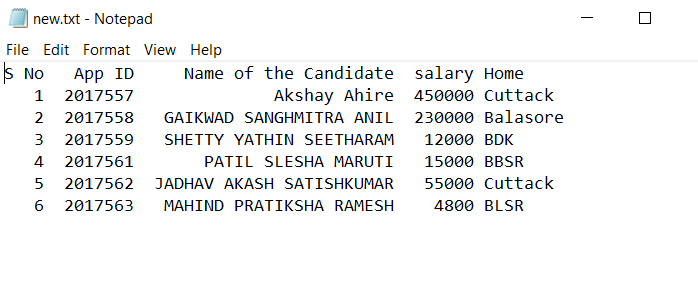
We will read this file with pandas.read_csv () method as follows.
import pandas as pd
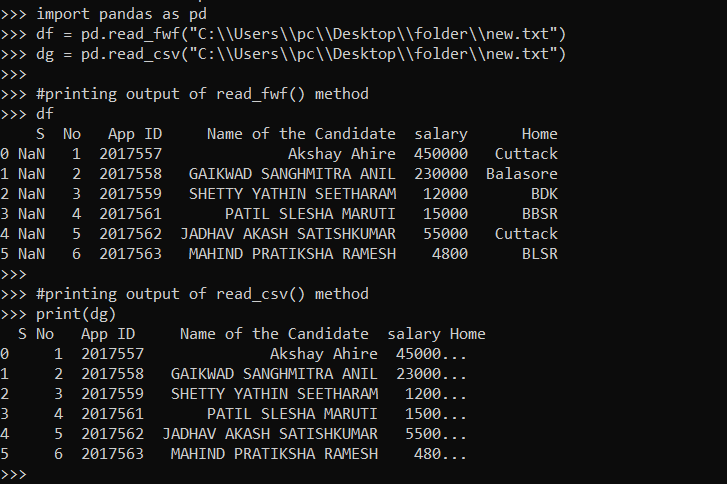
df = pd.read_csv("C:\\Users\\pc\\Desktop\\folder\\new.txt")
print(df)
In the above code snippet, We are trying to read a txt file containing a table. It will give the following output.
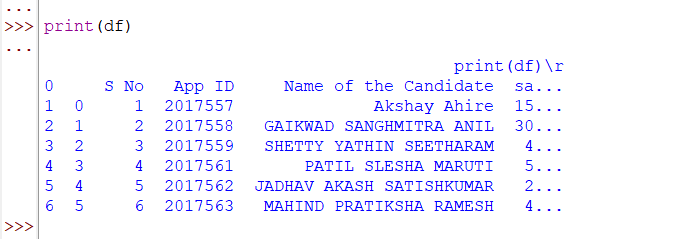
The most common drawback of using this method is that it reads limited contents in a single line. So in our output screen, The Home and Salary columns are not visible and partially visible respectively. To overcome this problem We are using the pandas.read_fwf () method. Let’s understand this method as well.
pandas.read_fwf ()
We use this method to access text files. The fwf stands for fixed-width lines. We will read data from the text files using this method with pandas. This read_fef() method read the contents effectively into separate columns.
Let us choose the same text file and we will try to access the file by using a different method (i.e. pandas.read_fwf() ).
import pandas as pd
#Using read_fwf() methd instead of read_csv()
df = pd.read_fwf("C:\\Users\\pc\\Desktop\\folder\\new.txt")
df
The above code snippet will give the output as follows.
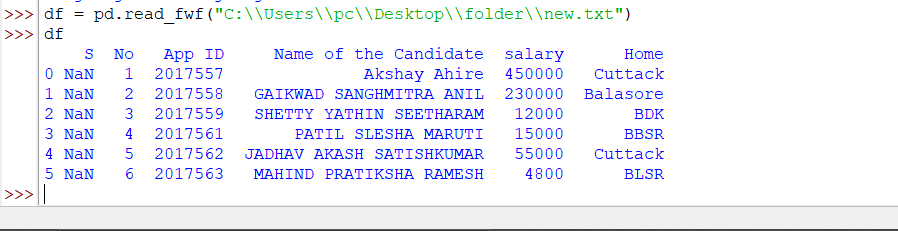
We can compare the outputs of read_fwf() and read_csv() method by analyzing the below outputs.
Conclusion
In this article, We covered two methods along with the pandas module to read a text file using Python. Hope You must have practiced and enjoyed our code snippets. We must visit again with some more exciting topics.





